티스토리 뷰
Problem
Given the root of a binary search tree, and an integer k, return the kth smallest value (1-indexed) of all the values of the nodes in the tree.
Example 1:
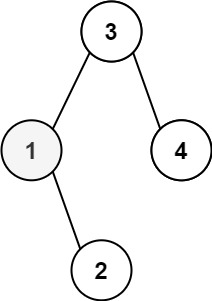
Input: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1
Output: 1Example 2:
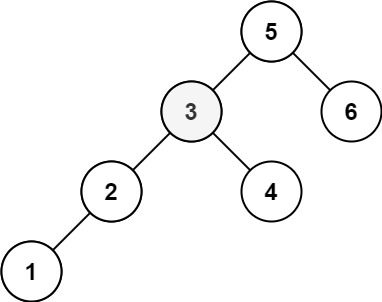
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3
Output: 3Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is n.
- 1 <= k <= n <= 10^4
- 0 <= Node.val <= 10^4
Follow up: If the BST is modified often (i.e., we can do insert and delete operations) and you need to find the kth smallest frequently, how would you optimize?
Solution
이진 트리의 root와 정수 k가 주어질 때 k번째로 작은 노드를 구하는 문제입니다.
stack을 이용해 풀 수 있습니다.
package io.lcalmsky.leetcode.kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst;
import io.lcalmsky.leetcode.TreeNode;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode node = root;
while (node != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
} else {
TreeNode pop = stack.pop();
k--;
if (k == 0) {
return pop.val;
}
node = pop.right;
}
}
return -1;
}
}Test
package io.lcalmsky.leetcode.kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst;
import io.lcalmsky.leetcode.TreeNode;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertAll;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
class SolutionTest {
@Test
void testAll() {
assertAll(
() -> test(TreeNode.of(3, 1, 4, null, 2), 1, 1),
() -> test(TreeNode.of(5, 3, 6, 2, 4, null, null, 1), 3, 3)
);
}
private void test(TreeNode root, int k, int expected) {
// when
Solution solution = new Solution();
int actual = solution.kthSmallest(root, k);
// then
assertEquals(expected, actual);
}
}TreeNode 클래스 보기
package io.lcalmsky.leetcode;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.StringJoiner;
public class TreeNode implements Cloneable{
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
public static TreeNode of(Integer... array) {
if (array == null || array.length == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
Queue<TreeNode> treeNodeQueue = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<Integer> integerQueue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
integerQueue.offer(array[i]);
}
TreeNode treeNode = new TreeNode(array[0]);
treeNodeQueue.offer(treeNode);
while (!integerQueue.isEmpty()) {
Integer leftVal = integerQueue.poll();
Integer rightVal = integerQueue.isEmpty() ? null : integerQueue.poll();
TreeNode current = treeNodeQueue.poll();
if (leftVal != null) {
TreeNode left = new TreeNode(leftVal);
assert current != null;
current.left = left;
treeNodeQueue.offer(left);
}
if (rightVal != null) {
TreeNode right = new TreeNode(rightVal);
assert current != null;
current.right = right;
treeNodeQueue.offer(right);
}
}
return treeNode;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return new StringJoiner(", ", TreeNode.class.getSimpleName() + "[", "]")
.add("val=" + val)
.add("left=" + left)
.add("right=" + right)
.toString();
}
public static void print(TreeNode treeNode) {
BTreePrinter.printNode(treeNode);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof TreeNode)) {
return false;
}
TreeNode treeNode = (TreeNode) o;
return val == treeNode.val &&
Objects.equals(left, treeNode.left) &&
Objects.equals(right, treeNode.right);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(val, left, right);
}
@Override
public TreeNode clone() {
try {
return (TreeNode) super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new AssertionError();
}
}
static class BTreePrinter {
public static void printNode(TreeNode root) {
int maxLevel = BTreePrinter.maxLevel(root);
printNodeInternal(Collections.singletonList(root), 1, maxLevel);
}
private static void printNodeInternal(List<TreeNode> nodes, int level, int maxLevel) {
if (nodes.isEmpty() || BTreePrinter.isAllElementsNull(nodes)) {
return;
}
int floor = maxLevel - level;
int edgeLines = (int) Math.pow(2, (Math.max(floor - 1, 0)));
int firstSpaces = (int) Math.pow(2, (floor)) - 1;
int betweenSpaces = (int) Math.pow(2, (floor + 1)) - 1;
BTreePrinter.printWhitespaces(firstSpaces);
List<TreeNode> newNodes = new ArrayList<>();
for (TreeNode node : nodes) {
if (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.val);
newNodes.add(node.left);
newNodes.add(node.right);
} else {
newNodes.add(null);
newNodes.add(null);
System.out.print(" ");
}
BTreePrinter.printWhitespaces(betweenSpaces);
}
System.out.println();
for (int i = 1; i <= edgeLines; i++) {
for (TreeNode node : nodes) {
BTreePrinter.printWhitespaces(firstSpaces - i);
if (node == null) {
BTreePrinter.printWhitespaces(edgeLines + edgeLines + i + 1);
continue;
}
if (node.left != null) {
System.out.print("/");
} else {
BTreePrinter.printWhitespaces(1);
}
BTreePrinter.printWhitespaces(i + i - 1);
if (node.right != null) {
System.out.print("\\");
} else {
BTreePrinter.printWhitespaces(1);
}
BTreePrinter.printWhitespaces(edgeLines + edgeLines - i);
}
System.out.println();
}
printNodeInternal(newNodes, level + 1, maxLevel);
}
private static void printWhitespaces(int count) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
private static int maxLevel(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
return Math.max(BTreePrinter.maxLevel(node.left), BTreePrinter.maxLevel(node.right)) + 1;
}
private static <T> boolean isAllElementsNull(List<T> list) {
for (Object object : list) {
if (object != null) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
}
'Algorithm > LeetCode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [LeetCode] 240. Search a 2D Matrix II (0) | 2023.07.01 |
|---|---|
| [LeetCode] 46. Permutations (0) | 2023.06.30 |
| [LeetCode] 334. Increasing Triplet Subsequence (0) | 2023.06.28 |
| [LeetCode] 328. Odd Even Linked List (0) | 2023.06.27 |
| [LeetCode] 322. Coin Change (0) | 2023.06.26 |
댓글
공지사항
최근에 올라온 글
최근에 달린 댓글
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
링크
TAG
- 헥사고날 아키텍처
- spring boot application
- Spring Boot JPA
- Jackson
- Linux
- 스프링 데이터 jpa
- JPA
- proto3
- JSON
- 함께 자라기
- Spring Data JPA
- 스프링 부트 튜토리얼
- Java
- 알고리즘
- gRPC
- 함께 자라기 후기
- 스프링부트
- r
- Spring Boot
- intellij
- 스프링 부트 애플리케이션
- QueryDSL
- spring boot app
- 스프링 부트
- Spring Boot Tutorial
- 클린 아키텍처
- leetcode
- 스프링 부트 회원 가입
- spring boot jwt
- @ManyToOne
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
글 보관함
