티스토리 뷰
Problem
We are given a list of (axis-aligned) rectangles. Each rectangle[i] = [xi1, yi1, xi2, yi2] , where (xi1, yi1) are the coordinates of the bottom-left corner, and (xi2, yi2) are the coordinates of the top-right corner of the ith rectangle.
Find the total area covered by all rectangles in the plane. Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
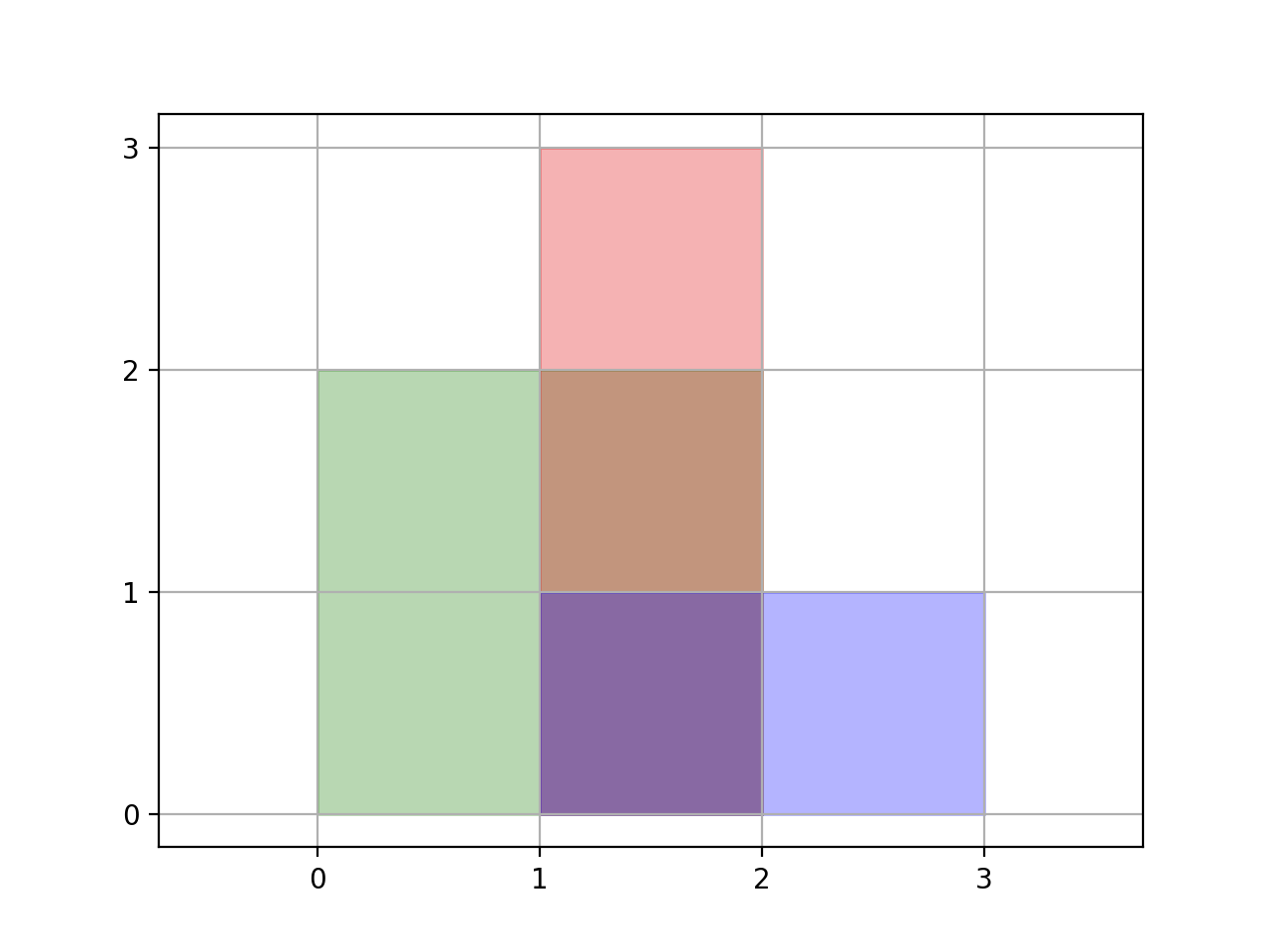
Example 1:
Input: rectangles = [[0,0,2,2],[1,0,2,3],[1,0,3,1]]
Output: 6
Explanation: As illustrated in the picture.Example 2:
Input: rectangles = [[0,0,1000000000,1000000000]]
Output: 49
Explanation: The answer is 1018 modulo (109 + 7), which is (109)2 = (-7)2 = 49.Constraints:
- 1 <= rectangles.length <= 200
- rectanges[i].length = 4
- 0 <= rectangles[i][j] <= 109
- The total area covered by all rectangles will never exceed 263 - 1 and thus will fit in a 64-bit signed integer.
Solution
List<int[]> all = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] rectangle : rectangles) {
helper(all, rectangle, 0);
}모든 직사각형을 첫 번 째 직사각형부터 순차적으로 비교합니다.
private void helper(List<int[]> all, int[] current, int start) {
if (start >= all.size()) {
all.add(current);
return;
}
// ...
}직사각형을 담을 리스트의 크기와 비교할 인덱스가 동일할 경우 현재 직사각형을 리스트에 추가하고 메서드를 종료합니다. 즉, 첫 번째로 추가된 직사각형의 경우 바로 리스트에 추가되고, 다음 직사각형부터 자기 자신과 비교할 때 추가됩니다.
예제로 주어진 직사각형 배열을 살펴보면
{0, 0, 2, 2}
{1, 0, 2, 3}
{1, 0, 3, 1}이 중 {0, 0, 2, 2}가 리스트에 추가되고 foreach 문의 다음 iteration이 수행됩니다.
두 번 째 직사각형인 {1, 0, 2, 3}를 비교할 때는 리스트에 이미 추가된 0번째 인덱스인 첫 번 째 직사각형과 비교합니다.
// ...
int[] rectangle = all.get(start);
if (current[RIGHT] <= rectangle[LEFT] || current[BOTTOM] <= rectangle[TOP] || current[LEFT] >= rectangle[RIGHT] || current[TOP] >= rectangle[BOTTOM]) {
helper(all, current, start + 1);
return;
}
if (current[LEFT] < rectangle[LEFT]) {
helper(all, new int[]{current[LEFT], current[TOP], rectangle[LEFT], current[BOTTOM]}, start + 1);
}
if (current[RIGHT] > rectangle[RIGHT]) {
helper(all, new int[]{rectangle[RIGHT], current[TOP], current[RIGHT], current[BOTTOM]}, start + 1);
}
if (current[TOP] < rectangle[TOP]) {
helper(all, new int[]{Math.max(rectangle[LEFT], current[LEFT]), current[TOP], Math.min(rectangle[RIGHT], current[RIGHT]), rectangle[TOP]}, start + 1);
}
if (current[BOTTOM] > rectangle[BOTTOM]) {
helper(all, new int[]{Math.max(rectangle[LEFT], current[LEFT]), rectangle[BOTTOM], Math.min(rectangle[RIGHT], current[RIGHT]), current[BOTTOM]}, start + 1);
}
}여기부터는 아래 규칙을 따릅니다.
현재 전달된 직사각형과 이미 리스트에 추가된 직사각형을 비교하면서
현재 직사각형이 이미 추가된 직사각형과 겹치지 않을 경우 다음 직사각형과의 비교를 위해 index 값을 올려준 뒤 재귀호출 합니다.
1번에 해당하지 않는 경우 한 군데라도 겹치는 부분이 있다는 것 이므로 겹치는 부분을 제외한 직사각형 만듧니다.
현재 직사각형의 왼쪽 좌표가 기존 직사각형의 왼쪽 좌표보다 작은 경우, 겹치지 않는 왼쪽 부분만 잘라서 새로운 직사각형을 만듦
new int[]{current[LEFT], current[TOP], rectangle[LEFT], current[BOTTOM]}기존 직사각형의 오른쪽 좌표가 현재 직사각형의 왼쪽 좌표로 대체됩니다.
현재 직사각형의 오른쪽 좌표가 기존 직사각형의 오른쪽 좌표보다 큰 경우, 겹치지 않는 오른쪽 부분만 잘라서 새로운 직사각형을 만듦
new int[]{rectangle[RIGHT], current[TOP], current[RIGHT], current[BOTTOM]}현재 직사각형의 왼쪽 좌표가 기존 직사각형의 오른쪽 좌표로 대체됩니다.
현재 직사각형의 위쪽 좌표가 기존 직사각형의 위쪽 좌표보다 큰 경우, 겹치지 않는 위쪽 부분만 잘라서 새로운 직사각형을 만듦
new int[]{Math.max(rectangle[LEFT], current[LEFT]), current[TOP], Math.min(rectangle[RIGHT], current[RIGHT]), rectangle[TOP]}현재 직사각형의 아래쪽 좌표를 기존 직사각형의 위쪽 좌표로 대체한 뒤, 좌우측 또한 겹치지 않는 부분을 추가합니다. 왼쪽의 경우 비교해서 큰 값으로, 오른쪽의 경우 비교해서 작은 값으로 추가해야 겹치지 않는 부분을 추가할 수 있습니다.
현재 직사각형의 아래쪽 좌표가 기존 직사각형의 아래쪽 좌표보다 작은 경우, 겹치지 않는 아래쪽 부분만 잘라서 새로운 직사각형을 만듦
new int[]{Math.max(rectangle[LEFT], current[LEFT]), rectangle[BOTTOM], Math.min(rectangle[RIGHT], current[RIGHT]), current[BOTTOM]}현재 직사각형의 위쪽 좌표를 기존 직사각형의 아래쪽 좌표로 대체한 뒤, 위에서 비교한 것 처럼 동일하게 비교하여 겹치지 않는 부분만 추가합니다.
다른 직사각형과의 비교를 위해
helper메서드를 재귀호출 하면서 새로 만든 직사각형과 증가한 index 값을 전달합니다.1~3의 작업이 순서대로 반복되면서 직사각형이 순차적으로 추가됩니다.
for (int[] subRectangle : all) {
result = (result + (long) (subRectangle[RIGHT] - subRectangle[LEFT]) * (long) (subRectangle[BOTTOM] - subRectangle[TOP])) % MODULO;
}추가된 직사각형을 순차적으로 참조하면서 각 넓이를 구해 modulo 값으로 나눠 결과에 더해줍니다.
Source Code
package io.lcalmsky.leetcode.rectangle_area_ii;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Solution {
public static final int LEFT = 0;
public static final int TOP = 1;
public static final int RIGHT = 2;
public static final int BOTTOM = 3;
private static final int MODULO = 1000000000 + 7;
public int rectangleArea(int[][] rectangles) {
long result = 0;
List<int[]> all = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] rectangle : rectangles) {
helper(all, rectangle, 0);
}
for (int[] subRectangle : all) {
result = (result + (long) (subRectangle[RIGHT] - subRectangle[LEFT]) * (long) (subRectangle[BOTTOM] - subRectangle[TOP])) % MODULO;
}
return (int) result;
}
private void helper(List<int[]> all, int[] current, int start) {
if (start >= all.size()) {
all.add(current);
return;
}
int[] rectangle = all.get(start);
if (current[RIGHT] <= rectangle[LEFT] || current[BOTTOM] <= rectangle[TOP] || current[LEFT] >= rectangle[RIGHT] || current[TOP] >= rectangle[BOTTOM]) {
helper(all, current, start + 1);
return;
}
if (current[LEFT] < rectangle[LEFT]) {
helper(all, new int[]{current[LEFT], current[TOP], rectangle[LEFT], current[BOTTOM]}, start + 1);
}
if (current[RIGHT] > rectangle[RIGHT]) {
helper(all, new int[]{rectangle[RIGHT], current[TOP], current[RIGHT], current[BOTTOM]}, start + 1);
}
if (current[TOP] < rectangle[TOP]) {
helper(all, new int[]{Math.max(rectangle[LEFT], current[LEFT]), current[TOP], Math.min(rectangle[RIGHT], current[RIGHT]), rectangle[TOP]}, start + 1);
}
if (current[BOTTOM] > rectangle[BOTTOM]) {
helper(all, new int[]{Math.max(rectangle[LEFT], current[LEFT]), rectangle[BOTTOM], Math.min(rectangle[RIGHT], current[RIGHT]), current[BOTTOM]}, start + 1);
}
}
}Test
package io.lcalmsky.leetcode.rectangle_area_ii;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertAll;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
class SolutionTest {
@Test
public void givenRectangles_whenFindTotalArea_thenCorrect() {
assertAll(
() -> test(new int[][]{
{0, 0, 2, 2},
{1, 0, 2, 3},
{1, 0, 3, 1}
}, 6),
() -> test(new int[][]{
{0, 0, 1000000000, 1000000000}
}, 49)
);
}
private void test(int[][] given, int expected) {
// when
Solution solution = new Solution();
int actual = solution.rectangleArea(given);
// then
assertEquals(expected, actual);
}
}'Algorithm > LeetCode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [LeetCode - Daily Challenge] 330. Patching Array (0) | 2021.08.30 |
|---|---|
| [LeetCode - Daily Challenge] 331. Verify Preorder Serialization of a Binary Tree (0) | 2021.08.27 |
| [LeetCode - Daily Challenge] 633. Sum of Square Numbers (0) | 2021.08.26 |
| [LeetCode - Daily Challenge] 537. Complex Number Multiplication (0) | 2021.08.25 |
| [LeetCode - Daily Challenge] 653. Two Sum IV - Input is a BST (0) | 2021.08.24 |
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- r
- leetcode
- QueryDSL
- JPA
- intellij
- 스프링 부트 튜토리얼
- 스프링 데이터 jpa
- 스프링 부트
- spring boot jwt
- 스프링 부트 애플리케이션
- gRPC
- 함께 자라기 후기
- proto3
- 헥사고날 아키텍처
- Spring Boot Tutorial
- Linux
- JSON
- 스프링 부트 회원 가입
- 스프링부트
- Spring Data JPA
- Spring Boot JPA
- spring boot application
- 클린 아키텍처
- spring boot app
- Java
- @ManyToOne
- Spring Boot
- 함께 자라기
- Jackson
- 알고리즘
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
