티스토리 뷰
Problem
Given the root of a binary search tree and the lowest and highest boundaries as low and high, trim the tree so that all its elements lies in [low, high]. Trimming the tree should not change the relative structure of the elements that will remain in the tree (i.e., any node's descendant should remain a descendant). It can be proven that there is a unique answer.
Return the root of the trimmed binary search tree. Note that the root may change depending on the given bounds.
Example 1:
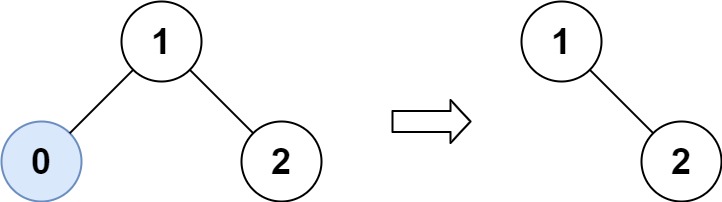
Input: root = [1,0,2], low = 1, high = 2
Output: [1,null,2]Example 2:
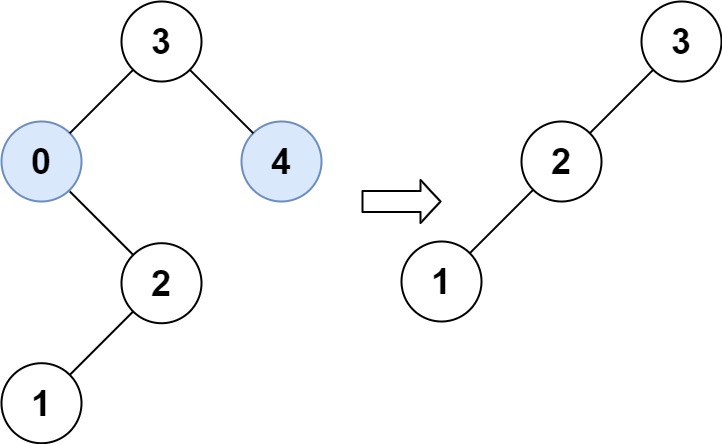
Input: root = [3,0,4,null,2,null,null,1], low = 1, high = 3
Output: [3,2,null,1]Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree in the range [1, 10^4].
- 0 <= Node.val <= 10^4
- The value of each node in the tree is unique.
- root is guaranteed to be a valid binary search tree.
- 0 <= low <= high <= 10^4
Solution
이진 트리와 작은 값과 큰 값의 범위가 주어질 때, 범위 안에 해당하는 노드만 잘라내는 문제입니다.
잘라낼 때도 기존 구조를 유지해야 합니다.
public class Solution {
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
if (root == null) { // (1)
return null;
}
if (root.val > high) { // (2)
return trimBST(root.left, low, high);
}
if (root.val < low) { // (3)
return trimBST(root.right, low, high);
}
// (4)
root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, root.val);
// (5)
root.right = trimBST(root.right, root.val, high);
return root;
}
}- 현재 노드가 null일 때 null을 반환합니다.
- 현재 노드의 값이 범위보다 클 때 현재 노드의 왼쪽 노드로 재귀호출 합니다.
- 현재 노드의 값이 범위보다 작을 때 현재 노드의 오른쪽 노드로 재귀호출 합니다.
- 현재 노드의 값이 범위 안에 들어갈 때 왼쪽 노드는 범위의 작은 값에서 현재 노드의 값까지 범위만큼만 재귀호출을 통해 다시 검사합니다.
- 현재 노드의 값이 범위 안에 들어갈 때 오른쪽 노드는 현재 노드의 값에서 범위의 큰 값까지 범위만큼만 재귀호출을 통해 다시 검사합니다.
TreeNode.java 전체 보기
package io.lcalmsky.leetcode;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.StringJoiner;
public class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
public static TreeNode of(Integer... array) {
if (array == null || array.length == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
Queue<TreeNode> treeNodeQueue = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<Integer> integerQueue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
integerQueue.offer(array[i]);
}
TreeNode treeNode = new TreeNode(array[0]);
treeNodeQueue.offer(treeNode);
while (!integerQueue.isEmpty()) {
Integer leftVal = integerQueue.poll();
Integer rightVal = integerQueue.isEmpty() ? null : integerQueue.poll();
TreeNode current = treeNodeQueue.poll();
if (leftVal != null) {
TreeNode left = new TreeNode(leftVal);
assert current != null;
current.left = left;
treeNodeQueue.offer(left);
}
if (rightVal != null) {
TreeNode right = new TreeNode(rightVal);
assert current != null;
current.right = right;
treeNodeQueue.offer(right);
}
}
return treeNode;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return new StringJoiner(", ", TreeNode.class.getSimpleName() + "[", "]")
.add("val=" + val)
.add("left=" + left)
.add("right=" + right)
.toString();
}
public static void print(TreeNode treeNode) {
BTreePrinter.printNode(treeNode);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof TreeNode)) {
return false;
}
TreeNode treeNode = (TreeNode) o;
return val == treeNode.val &&
Objects.equals(left, treeNode.left) &&
Objects.equals(right, treeNode.right);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(val, left, right);
}
static class BTreePrinter {
public static void printNode(TreeNode root) {
int maxLevel = BTreePrinter.maxLevel(root);
printNodeInternal(Collections.singletonList(root), 1, maxLevel);
}
private static void printNodeInternal(List<TreeNode> nodes, int level, int maxLevel) {
if (nodes.isEmpty() || BTreePrinter.isAllElementsNull(nodes)) {
return;
}
int floor = maxLevel - level;
int edgeLines = (int) Math.pow(2, (Math.max(floor - 1, 0)));
int firstSpaces = (int) Math.pow(2, (floor)) - 1;
int betweenSpaces = (int) Math.pow(2, (floor + 1)) - 1;
BTreePrinter.printWhitespaces(firstSpaces);
List<TreeNode> newNodes = new ArrayList<>();
for (TreeNode node : nodes) {
if (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.val);
newNodes.add(node.left);
newNodes.add(node.right);
} else {
newNodes.add(null);
newNodes.add(null);
System.out.print(" ");
}
BTreePrinter.printWhitespaces(betweenSpaces);
}
System.out.println();
for (int i = 1; i <= edgeLines; i++) {
for (TreeNode node : nodes) {
BTreePrinter.printWhitespaces(firstSpaces - i);
if (node == null) {
BTreePrinter.printWhitespaces(edgeLines + edgeLines + i + 1);
continue;
}
if (node.left != null) {
System.out.print("/");
} else {
BTreePrinter.printWhitespaces(1);
}
BTreePrinter.printWhitespaces(i + i - 1);
if (node.right != null) {
System.out.print("\\");
} else {
BTreePrinter.printWhitespaces(1);
}
BTreePrinter.printWhitespaces(edgeLines + edgeLines - i);
}
System.out.println();
}
printNodeInternal(newNodes, level + 1, maxLevel);
}
private static void printWhitespaces(int count) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
private static int maxLevel(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
return Math.max(BTreePrinter.maxLevel(node.left), BTreePrinter.maxLevel(node.right)) + 1;
}
private static <T> boolean isAllElementsNull(List<T> list) {
for (Object object : list) {
if (object != null) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
}
Test
package io.lcalmsky.leetcode.trim_a_binary_search_tree;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertAll;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import io.lcalmsky.leetcode.TreeNode;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
class SolutionTest {
@Test
void givenBinarySearchTree_whenTrimTreeThatItsElementsLiesBetweenLowAndHigh_thenCorrect() {
assertAll(
() -> test(TreeNode.of(1, 0, 2), 1, 2, TreeNode.of(1, null, 2)),
() -> test(TreeNode.of(3, 0, 4, null, 2, null, null, 1), 1, 3, TreeNode.of(3, 2, null, 1)),
() -> test(TreeNode.of(1), 1, 2, TreeNode.of(1)),
() -> test(TreeNode.of(1, null, 2), 1, 3, TreeNode.of(1, null, 2)),
() -> test(TreeNode.of(1, null, 2), 2, 4, TreeNode.of(2))
);
}
private void test(TreeNode root, int low, int high, TreeNode expected) {
// when
Solution solution = new Solution();
TreeNode actual = solution.trimBST(root, low, high);
// then
assertEquals(expected, actual);
}
}'Algorithm > LeetCode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 410. Split Array Largest Sum (0) | 2022.05.03 |
|---|---|
| 897. Increasing Order Search Tree (0) | 2022.04.30 |
| 81. Search in Rotated Sorted Array II (0) | 2022.04.28 |
| 700. Search in a Binary Search Tree (0) | 2022.04.27 |
| 991. Broken Calculator (0) | 2022.04.26 |
댓글
공지사항
최근에 올라온 글
최근에 달린 댓글
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
링크
TAG
- proto3
- spring boot application
- 알고리즘
- 헥사고날 아키텍처
- leetcode
- 스프링 부트 회원 가입
- 스프링부트
- Linux
- Spring Boot Tutorial
- Java
- 함께 자라기 후기
- Spring Data JPA
- JPA
- Spring Boot JPA
- spring boot app
- 스프링 데이터 jpa
- intellij
- 클린 아키텍처
- 스프링 부트 튜토리얼
- @ManyToOne
- QueryDSL
- 스프링 부트
- r
- spring boot jwt
- JSON
- 스프링 부트 애플리케이션
- 함께 자라기
- Spring Boot
- gRPC
- Jackson
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
글 보관함
