티스토리 뷰
Problem
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order, and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example 1:
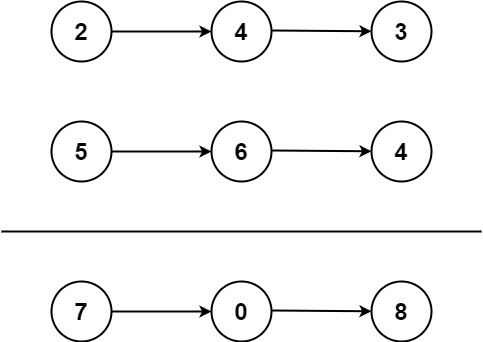
Input: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
Output: [7,0,8]
Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.Example 2:
Input: l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
Output: [0]Example 3:
Input: l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]
Output: [8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range [1, 100].
- 0 <= Node.val <= 9
- It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.
Solution
두 개의 양의 정수를 나타내는 연결 리스트가 주어지고, 연결 리스트에 숫자들은 역순으로 저장되어있을 때 두 수의 합을 구하는 문제입니다.
0으로 시작하는 숫자는 0을 제외하고는 주어지지 않습니다.
import io.lcalmsky.leetcode.ListNode;
public class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = l1, q = l2, current = dummyHead;
int carry = 0;
while (p != null || q != null) {
int x = (p != null) ? p.val : 0; // (1)
int y = (q != null) ? q.val : 0; // (2)
int sum = carry + x + y; // (3)
carry = sum / 10; // (4)
current.next = new ListNode(sum % 10); // (5)
current = current.next; // (6)
if (p != null) { // (7)
p = p.next;
}
if (q != null) { // (8)
q = q.next;
}
}
if (carry > 0) { // (9)
current.next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return dummyHead.next; // (10
}
}- l1의 현재 값을 구합니다.
- l2의 현재 값을 구합니다.
- l1, l2의 현재 노드의 합을 구합니다.
- 받아 올림 값을 구합니다.
- 다음 노드를 추가합니다.
- 현재 노드를 이동시킵니다.
- l1의 현재 노드를 이동시킵니다.
- l2의 현재 노드를 이동시킵니다.
- 받아 올림 값이 남아있을 경우 노드를 추가합니다.
- 처음에 dummy 값을 생성했으므로 다음 노드부터가 정답이 됩니다.
Test
package io.lcalmsky.leetcode.add_two_numbers;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertAll;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import io.lcalmsky.leetcode.ListNode;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
class SolutionTest {
@Test
void testAll() {
assertAll(
() -> test(ListNode.of(2, 4, 3), ListNode.of(5, 6, 4), ListNode.of(7, 0, 8)),
() -> test(ListNode.of(0), ListNode.of(0), ListNode.of(0)),
() -> test(ListNode.of(9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9), ListNode.of(9, 9, 9, 9),
ListNode.of(8, 9, 9, 9, 0, 0, 0, 1))
);
}
private void test(ListNode l1, ListNode l2, ListNode expected) {
// when
Solution solution = new Solution();
ListNode actual = solution.addTwoNumbers(l1, l2);
// then
assertEquals(expected, actual);
}
}ListNode.java 전체 보기
package io.lcalmsky.leetcode;
import java.util.Objects;
public class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
public static ListNode of(int... integers) {
if (integers == null || integers.length == 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode last = head;
ListNode p;
for (int integer : integers) {
p = new ListNode(integer);
last.next = p;
last = last.next;
}
return head.next;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ListNode{" +
"val=" + val +
", next=" + next +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof ListNode)) return false;
ListNode listNode = (ListNode) o;
return val == listNode.val &&
Objects.equals(next, listNode.next);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(val, next);
}
}'Algorithm > LeetCode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 20. Valid Parentheses (0) | 2022.03.20 |
|---|---|
| 61. Rotate List (0) | 2022.03.19 |
| 82. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II (0) | 2022.03.17 |
| 413. Arithmetic Slices (0) | 2022.03.15 |
| 141. Linked List Cycle (0) | 2022.03.14 |
댓글
공지사항
최근에 올라온 글
최근에 달린 댓글
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
링크
TAG
- spring boot application
- 클린 아키텍처
- 스프링 부트 튜토리얼
- spring boot app
- JPA
- r
- proto3
- QueryDSL
- 스프링 부트 회원 가입
- gRPC
- 함께 자라기 후기
- 함께 자라기
- 스프링 부트 애플리케이션
- Spring Boot
- 헥사고날 아키텍처
- spring boot jwt
- Linux
- 알고리즘
- JSON
- intellij
- leetcode
- Java
- Jackson
- Spring Boot JPA
- 스프링 데이터 jpa
- Spring Data JPA
- @ManyToOne
- 스프링 부트
- Spring Boot Tutorial
- 스프링부트
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
글 보관함
