티스토리 뷰
Problem
Given the head of a linked list, return the list after sorting it in ascending order.
Example 1:
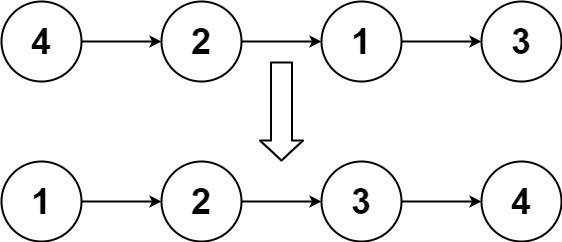
Input: head = [4,2,1,3]
Output: [1,2,3,4]Example 2:

Input: head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
Output: [-1,0,3,4,5]Example 3:
Input: head = []
Output: []Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 5 * 104].
- -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
Follow up: Can you sort the linked list in O(n logn) time and O(1) memory (i.e. constant space)?
Solution
연결 리스트의 head가 주어질 때 해당 리스트를 오름차순으로 정렬하는 문제입니다.
그냥 푼다고 생각하면 단순히 리스트 같은 데 데이터를 옮긴 뒤 정렬할 수 있겠지만 O(n log n)의 시간 복잡도와 O(1) 공간 복잡도로 해결할 수 있는지 묻고있습니다.
다양한 정렬 알고리즘이 존재하지만 위 조건에 부합하는 것은 바로 MergeSort 입니다.
QuickSort 또한 평균 시간 복잡도가 O(n log n)이지만 워스트 케이스의 경우 O(n^2)이 됩니다.
randomized quicksort 같은 경우 배열이 아닌 linked list 정렬에는 적합하지 않습니다. 그 이유는 공간 복잡도를 O(1)로 수행할 수 없기 때문입니다.
두 가지 접근 방법이 있습니다.
Top Down Merge Sort
Merge Sort는 분할정복 알고리즘으로 잘 알려져 있습니다. 분할, 정복 과정은 두 개의 구간으로 나눌 수 있습니다.
- 분할 구간: 문제를 부분 문제로 나눔
- 정복 구간: 반복적으로 독립적인 부분 문제들을 해결한 뒤 원래 문제로 결합시킴
탑다운 방식의 merge sort는 재귀적으로 기존 리스트를 같은 사이즈의 부분 리스트로 나눈뒤, 각각의 부분 리스트를 정렬하고, 정렬된 리스트를 합병합니다.
import io.lcalmsky.leetcode.ListNode;
public class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode mid = getMid(head);
ListNode left = sortList(head);
ListNode right = sortList(mid);
return merge(left, right);
}
ListNode getMid(ListNode head) {
ListNode midPrev = null;
while (head != null && head.next != null) {
midPrev = midPrev == null ? head : midPrev.next;
head = head.next.next;
}
ListNode mid = midPrev.next;
midPrev.next = null;
return mid;
}
ListNode merge(ListNode left, ListNode right) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode tail = dummyHead;
while (left != null && right != null) {
if (left.val < right.val) {
tail.next = left;
left = left.next;
} else {
tail.next = right;
right = right.next;
}
tail = tail.next;
}
tail.next = (left != null) ? left : right;
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
ListNode.java 전체 보기
package io.lcalmsky.leetcode;
import java.util.Objects;
public class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
public static ListNode of(int... integers) {
if (integers == null || integers.length == 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode last = head;
ListNode p;
for (int integer : integers) {
p = new ListNode(integer);
last.next = p;
last = last.next;
}
return head.next;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ListNode{" +
"val=" + val +
", next=" + next +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof ListNode)) return false;
ListNode listNode = (ListNode) o;
return val == listNode.val &&
Objects.equals(next, listNode.next);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(val, next);
}
}Test
package io.lcalmsky.leetcode.sort_list;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertAll;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import io.lcalmsky.leetcode.ListNode;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
class SolutionTest {
@Test
void testAll() {
assertAll(
() -> test(ListNode.of(4, 2, 1, 3), ListNode.of(1, 2, 3, 4)),
() -> test(ListNode.of(-1, 5, 3, 4, 0), ListNode.of(-1, 0, 3, 4, 5)),
() -> test(null, null)
);
}
private void test(ListNode given, ListNode expected) {
// when
Solution solution = new Solution();
ListNode actual = solution.sortList(given);
// then
assertEquals(expected, actual);
}
}'Algorithm > LeetCode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 24. Swap Nodes in Pairs (0) | 2022.03.04 |
|---|---|
| 662. Maximum Width of Binary Tree (0) | 2022.03.03 |
| 169. Majority Element (0) | 2022.02.28 |
| 1288. Remove Covered Intervals (0) | 2022.02.27 |
| 1675. Minimize Deviation in Array (0) | 2022.02.26 |
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- Linux
- leetcode
- JPA
- 함께 자라기 후기
- 스프링 부트 회원 가입
- 스프링 부트 애플리케이션
- spring boot app
- 함께 자라기
- intellij
- Spring Data JPA
- 헥사고날 아키텍처
- QueryDSL
- 스프링 데이터 jpa
- r
- 스프링 부트 튜토리얼
- 스프링부트
- JSON
- Spring Boot Tutorial
- proto3
- spring boot application
- 스프링 부트
- gRPC
- spring boot jwt
- @ManyToOne
- Java
- Jackson
- Spring Boot
- Spring Boot JPA
- 알고리즘
- 클린 아키텍처
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
