티스토리 뷰
모든 소스는 여기서 확인하실 수 있습니다.
Jackson Serialization
jackson이 제공하는 직렬화(serialization) 애노테이션에 대해 알아봅시다.
@JsonAnyGetter
Map 필드를 표준 property로 사용할 수 있는 유연성을 제공합니다.
package io.lcalmsky.jackson_test.domain;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAnyGetter;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ExtendableBean {
public String name;
private Map<String, Object> properties;
public ExtendableBean(String name) {
this.name = name;
this.properties = new HashMap<>();
}
@JsonAnyGetter
public Map<String, Object> getProperties() {
return properties;
}
public void add(String key, Object value) {
properties.put(key, value);
}
}package io.lcalmsky.jackson.domain;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.containsString;
import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertAll;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
public class ExtendableBeanTests {
@Test
@DisplayName("JsonAnyGetter를 사용하여 JSON 작성하기")
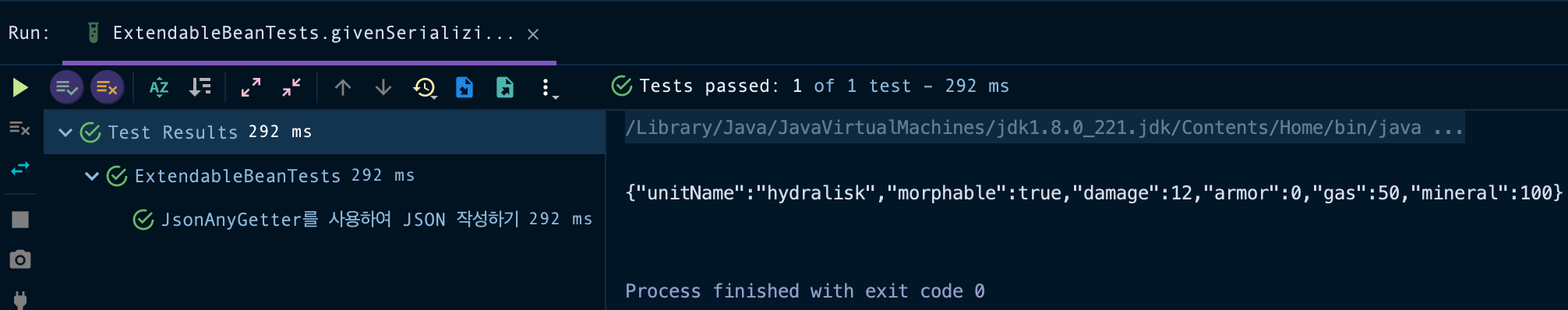
public void givenSerializingUsingJsonAnyGetter_whenWriteJson_thenCorrect() throws JsonProcessingException {
// given
ExtendableBean bean = new ExtendableBean("hydralisk");
bean.add("mineral", 100);
bean.add("gas", 50);
bean.add("morphable", true);
bean.add("damage", 12);
bean.add("armor", 0);
// when
String result = new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(bean);
// then
assertAll(
() -> assertThat(result, containsString("mineral")),
() -> assertThat(result, containsString("gas")),
() -> assertThat(result, containsString("morphable")),
() -> assertThat(result, containsString("damage")),
() -> assertThat(result, containsString("armor"))
);
// log
System.out.println(result);
}
}
@JsonGetter
@JsonProperty를 대신하여 getter 메소드에 사용하는 애노테이션 입니다.
바로 위에서 사용했던 ExtendableBean 클래스에 아래와 같은 메소드를 추가한 뒤 동일한 테스트를 실행시켜보면
@JsonGetter
public String getUnitName() {
return this.name;
}{"unitName":"hydralisk","morphable":true,"damage":12,"armor":0,"gas":50,"mineral":100}
키 값이 바뀐 것을 확인하실 수 있습니다.
@JsonPropertyOrder
직렬화 할 때 property의 순서를 지정할 수 있는 애노테이션 입니다.
package io.lcalmsky.jackson_test.domain;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonPropertyOrder;
@JsonPropertyOrder({"name", "age", "id"})
public class OrderedBean {
private String id;
private String name;
private int age;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
package io.lcalmsky.jackson.domain;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.UUID;
public class OrderedBeanTests {
@Test
@DisplayName("@JsonPropertyOrder 적용한 뒤 순서 확인")
public void givenOrderedBeanUsingJsonPropertyOrder_whenWriteJson_thenOrderedJson() throws JsonProcessingException {
// given
OrderedBean orderedBean = new OrderedBean();
orderedBean.setId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
orderedBean.setName("홍길동");
orderedBean.setAge(30);
// when
String json = new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(orderedBean);
// then
System.out.println(json);
}
}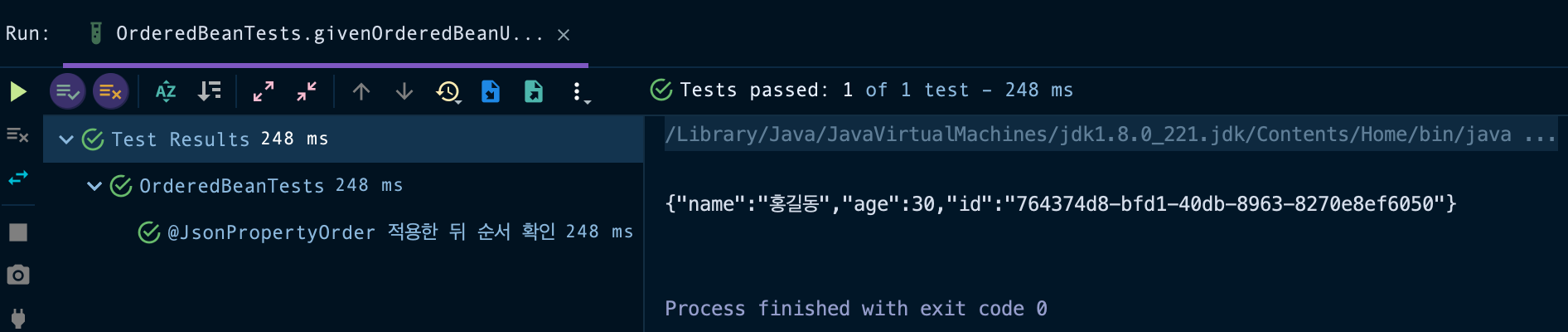
{"name":"홍길동","age":30,"id":"3e824dc5-10d8-4bfe-822f-1b3432f20231"}
애노테이션에 명시한대로 name, age, id 순서로 JSON이 생성되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
@JsonRawValue
Jackson이 속성을 그대로 직렬화하도록 하는 애노테이션 입니다.
package io.lcalmsky.jackson_test.domain;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonRawValue;
public class RawBean {
private String name;
@JsonRawValue
private String json;
public RawBean(String name, String json) {
this.name = name;
this.json = json;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getJson() {
return json;
}
}
package io.lcalmsky.jackson.domain;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
public class RawBeanTests {
@Test
@DisplayName("JSON값 그대로 직렬화한뒤 확인")
public void givenJsonRawValueApplied_whenWriteJson_thenRawValue() throws JsonProcessingException {
// given
RawBean bean = new RawBean("My bean", "{\"attr\":false}");
// when
String result = new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(bean);
// then
assertTrue(result.contains("My bean"));
assertTrue(result.contains("{\"attr\":false}"));
// log
System.out.println(result);
}
}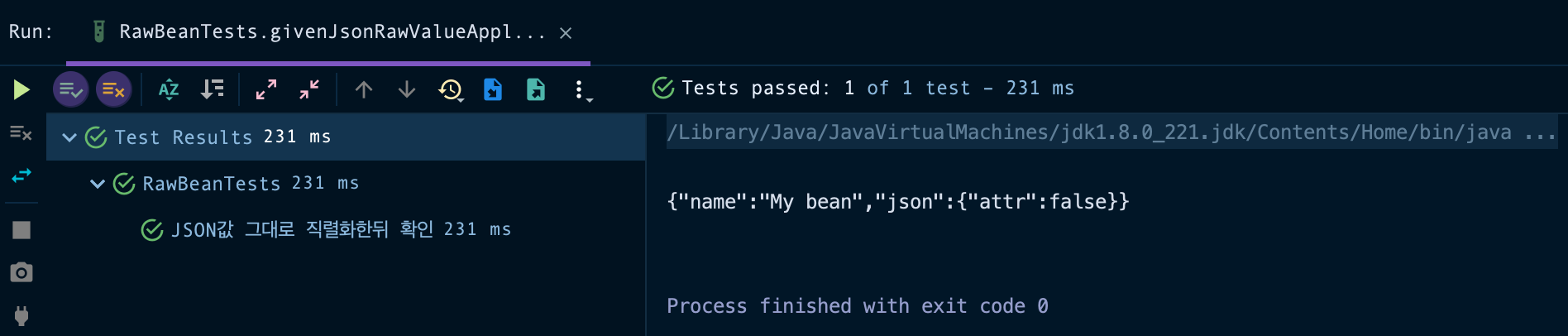
{"name":"My bean","json":{"attr":false}}
@JsonValue
인스턴스 직렬화를 위해 사용하는 메소드를 지정합니다.
package io.lcalmsky.jackson_test.domain.support;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonValue;
public enum EnumWithValue {
ENUM1(1, "TYPE1"),
ENUM2(2, "TYPE2");
private Integer intValue;
private String strValue;
private EnumWithValue(Integer intValue, String strValue) {
this.intValue = intValue;
this.strValue = strValue;
}
@JsonValue
public Integer getIntValue() {
return intValue;
}
public String getStrValue() {
return strValue;
}
}
package io.lcalmsky.jackson.domain.support;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
public class EnumWithValueTests {
@Test
@DisplayName("@JsonValue를 사용하여 enum 타입을 직렬화하기")
public void givenJsonValueApplied_whenSerialize_thenCorrect() throws JsonProcessingException {
// given
EnumWithValue enum1 = EnumWithValue.ENUM1;
// when
String enumValue = new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(enum1);
// then
assertEquals("1", enumValue);
// log
System.out.println(enumValue);
}
}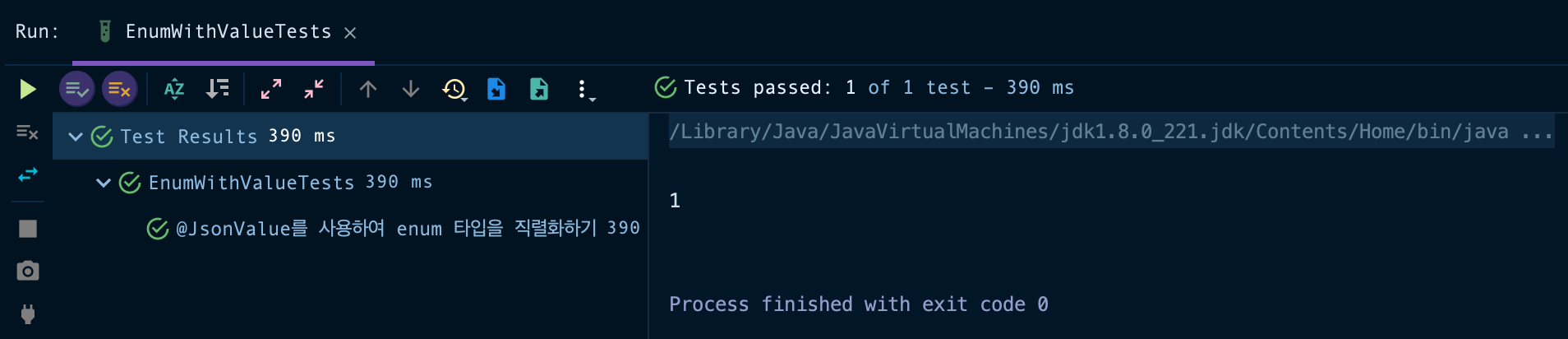
@JsonValue를 getIntValue()에 지정하였으므로 EnumWithValue 타입의 객체 ENUM1를 역직렬화하였을 때 intValue인 "1"로 변환(writeValueAsString 메소드를 사용하였으므로 정수로 사용하려면 형변환 필요)됩니다. @JsonValue를 getStrValue()에 지정하였다면 "TYPE1"로 변환되었겠죠!
@JsonSerialize
객체로 직렬화 할 때 커스텀 시리얼라이저를 사용하겠다는 애노테이션 입니다.
package io.lcalmsky.jackson_test.domain;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.annotation.JsonSerialize;
import io.lcalmsky.jackson_test.domain.serializer.CustomDateSerializer;
import java.time.LocalDate;
public class BeanWithSerializer {
private String name;
@JsonSerialize(using = CustomDateSerializer.class)
private LocalDate time;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public LocalDate getTime() {
return time;
}
public void setTime(LocalDate time) {
this.time = time;
}
}
package io.lcalmsky.jackson_test.domain.serializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonGenerator;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonSerializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.SerializerProvider;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.time.LocalDate;
public class CustomDateSerializer extends JsonSerializer<LocalDate> {
@Override
public void serialize(LocalDate value, JsonGenerator gen, SerializerProvider serializers) throws IOException {
gen.writeString(String.format("%s년 %s월 %s일", value.getYear(), value.getMonthValue(), value.getDayOfMonth()));
}
}
package io.lcalmsky.jackson.domain;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
public class BeanWithSerializerTests {
@Test
@DisplayName("CustomSerializer를 사용해 역직렬화하기")
public void givenUsingCustomSerializer_whenWriteJson_thenCorrect() throws JsonProcessingException {
// given
BeanWithSerializer beanWithSerializer = new BeanWithSerializer();
beanWithSerializer.setName("날짜");
beanWithSerializer.setTime(LocalDate.of(2019, 11, 15));
// when
String json = new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(beanWithSerializer);
// then
assertTrue(json.contains("2019년 11월 15일"));
// log
System.out.println(json);
}
}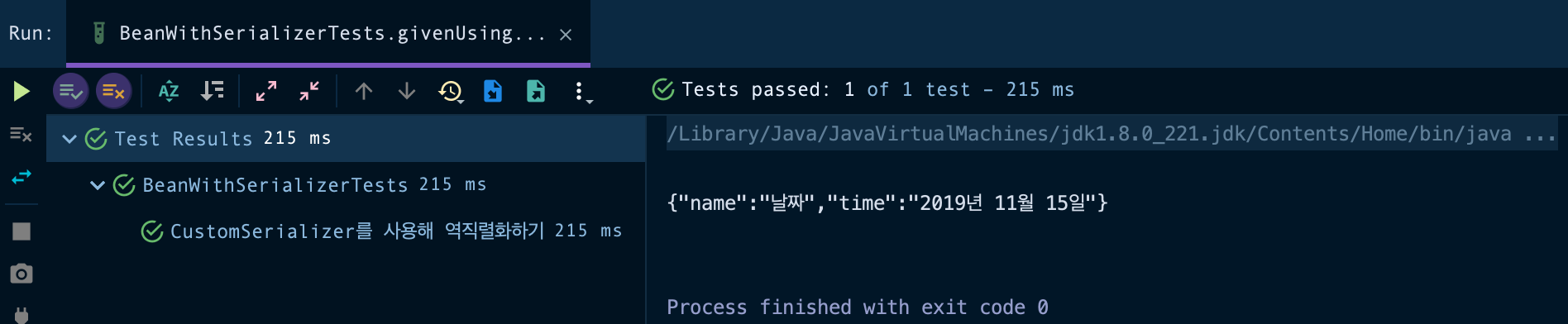
LocalDate 값을 yyyy년 MM월 DD일 형식으로 출력하는 것을 확인하실 수 있습니다. 꼭 커스텀 시리얼라이저를 지정하지 않아도 기본으로 제공하는 시리얼라이저를 사용하실 수도 있습니다.
다음 포스팅은 역직렬화(Deserialization) 애노테이션에 대해 확인해보겠습니다.
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Jackson의 모든 것 - 커스터마이징 편 (0) | 2019.11.26 |
|---|---|
| Jackson의 모든 것 - 일반편 (0) | 2019.11.22 |
| Jackson의 모든 것 - 다형성 편 (0) | 2019.11.21 |
| Jackson의 모든 것 - Property 편 (0) | 2019.11.20 |
| Jackson의 모든 것 - 역 직렬화 편 (0) | 2019.11.19 |
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- proto3
- Java
- r
- intellij
- gRPC
- Jackson
- QueryDSL
- @ManyToOne
- Spring Boot
- JPA
- 스프링 부트
- 스프링 부트 튜토리얼
- 스프링 부트 회원 가입
- 스프링 부트 애플리케이션
- 스프링부트
- Spring Boot JPA
- 함께 자라기 후기
- 함께 자라기
- spring boot jwt
- Linux
- 스프링 데이터 jpa
- 클린 아키텍처
- 헥사고날 아키텍처
- Spring Boot Tutorial
- spring boot application
- 알고리즘
- leetcode
- Spring Data JPA
- JSON
- spring boot app
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 |
